Catalog
• How Does D882 Transistor Work
• D882 Transistor Applications (Uses)
• D882 Transistor Equivalent (Alternative) Parts
• Where to Buy D882 Transistor
• Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
Introduction to D882
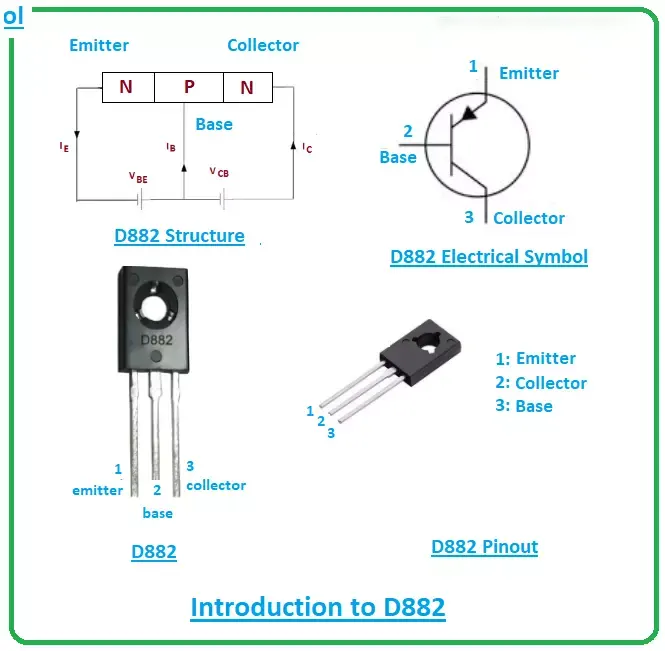
The D882 transistor is an essential component in the world of electronics, serving as a robust and versatile NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT). Primarily designed for low to medium-frequency power amplification and switching operations, the D882 has found its place in countless applications from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. Manufactured by various semiconductor giants like Fairchild and ON Semiconductor, its popularity stems from its cost-effectiveness, high availability, and reliable performance.
Unlike many other BJTs that either offer high voltage with low current or vice versa, the D882 strikes a balanced middle ground. It allows designers to confidently handle moderate currents while maintaining efficient control, making it a backbone for many analog and power circuitry designs. Its reliable performance, simple integration, and affordable cost make it a practical option when you need efficient power management, accurate signal amplification, and dependable switching.
When you require a transistor that can withstand reasonable thermal and electrical stress without blowing your budget, the D882 becomes an obvious choice.
D882 Transistor Specs
Since its introduction, the D882 transistor has evolved from a simple, affordable switch into a trusted workhorse in electronic design. Originally designed to meet the growing demand for reliable mid-power switching and amplification in the late 20th century, the D882 has adapted through improvements in material quality, manufacturing precision, and thermal management technologies.
Even in 2025 and beyond, the D882 continues to appear in new schematics, especially in applications demanding medium current handling, decent switching speed, and robustness at a low BOM cost. It’s a testimony to smart, resilient engineering that values practical utility over sheer performance specs.
Let's dive deeper into the key specifications of the D882 transistor, which reveal its true strengths:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Transistor Type | NPN |
| Maximum Collector Current (Ic) | 3A |
| Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vce) | 30V |
| Maximum Collector-Base Voltage (Vcb) | 40V |
| Maximum Emitter-Base Voltage (Veb) | 5V |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) | 40 to 400 |
| Maximum Power Dissipation (Pd) | 1W to 10W (depending on cooling) |
| Transition Frequency (fT) | 100MHz |
| Package Type | TO-126 |
One standout feature is the high transition frequency (fT) of 100MHz, which allows the D882 to comfortably operate not just in low-frequency amplification but also in relatively fast switching circuits where response time matters. Unlike many other "legacy" transistors that faded with advancing technology, the D882 survived by striking a unique balance—offering just enough performance headroom for engineers while remaining cost-effective for mass production. It didn't try to compete with high-end RF or power transistors; instead, it perfected the middle ground.
D882 Transistor Features
The D882 transistor stands out for its versatility and performance in a wide range of applications, particularly in low to medium-power amplification and switching circuits. Here’s a deeper dive into the distinctive features of the D882 transistor. While many transistors seem similar on paper, the D882 carries features that set it apart for mid-power designs:
• Medium-Power Handling: Handles up to 3A continuously without significant performance degradation.
• High Transition Frequency: Suitable for fast-switching circuits that require sharp turn-on/turn-off responses.
• Wide Current Gain Range: Enables flexibility in amplification stages; useful for both low and moderate gain applications.
• Good Thermal Stability: Essential for circuits with prolonged operation under varying thermal conditions.
• Compact Size: TO-126 package offers a balance between small footprint and efficient heat dissipation.
• Availability and Cost: Its mass production ensures low cost and worldwide availability, even in shortage situations.
The D882 transistor is a well-balanced and robust component that offers a variety of features suited for both analog amplification and digital switching applications. Its thermal stability, medium-power handling, and cost-effectiveness make it a go-to choice for a broad spectrum of designs, especially where reliability and performance are key.
Whether you're working on audio systems, motor control circuits, or power regulators, the D882 is a versatile, high-performance transistor that continues to meet the evolving needs of electronics engineers across industries.
Unlike many similar-rated transistors, the D882 rarely suffers from "thermal runaway" issues when properly heatsinked, making it favored in designs where reliability over time is a key requirement.
D882 Transistor Pinout

Understanding the pin configuration of the D882 transistor is essential for correctly integrating it into your circuit. The D882 is an NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT), and its pinout follows the standard configuration for TO-126 packages.
When working with the D882, always ensure that the base pin is connected to the controlling signal, the collector to the load or output, and the emitter to ground or the negative terminal of the power supply. Properly handling the pin connections will ensure the transistor operates efficiently without issues like thermal runaway or performance degradation.
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
| 1 | Base | Controls the transistor's ON/OFF state |
| 2 | Collector | Load connection; main current flows through here when switched ON |
| 3 | Emitter | Connected to ground or negative terminal for NPN operation |
Pinout Diagram:
_______
| |
Base --|1 3|-- Emitter
| |
Collector
|___2___|
When working with the D882 in high-current applications, ensure a clean, low-resistance solder connection at the emitter lead to avoid parasitic resistance causing performance losses.
D882 Datasheet
The D882 transistor, being a popular NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT), has a well-documented datasheet. This datasheet contains critical information about its electrical characteristics, ratings, and operating conditions, helping designers effectively integrate it into their circuits.
Here's an overview of critical parameters straight from typical D882 datasheets:
| Absolute Maximum Ratings | Symbol | Value | Unit |
| Collector-Base Voltage | Vcbo | 40 | V |
| Collector-Emitter Voltage | Vceo | 30 | V |
| Emitter-Base Voltage | Vebo | 5 | V |
| Collector Current | Ic | 3 | A |
| Power Dissipation | Pd | 1-10 | W |
| Transition Frequency | fT | 100 | MHz |
| Operating Temp Range | Tj | -55 to +150 | °C |
When reading datasheets, always pay attention not just to max ratings but also "safe operating area" (SOA) graphs. For the D882, staying within recommended operating regions dramatically improves long-term reliability.
How Does D882 Transistor Work
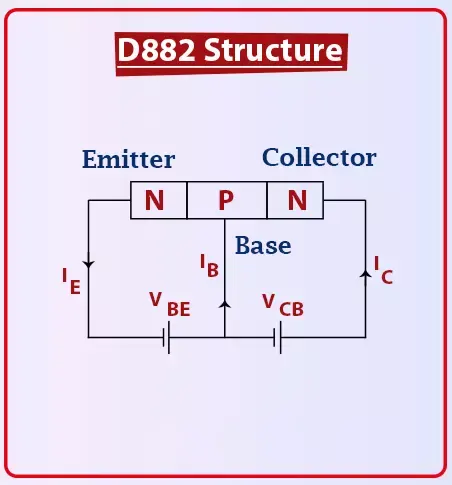
The overall transistor action starts from the base pin. The base terminal behaves like a control valve that controls the number of electrons emitted from the emitter terminal which are then collected by the collector terminal that is coupled with a resistor to control the electrical current.
Recall, in the NPN transistor the positive voltage supply is applied at the base terminal. The P-doped layer in the NPN transistor represents the base terminal and the other two n-doped layers represent emitter and collector terminals which are negative.
At its core, the D882 functions by using a small input current at its base to control a much larger current flowing from collector to emitter. Here's a deeper look:
• Base Current (Ib): A small current injected here triggers the transistor.
• Collector Current (Ic): Controlled by the base current. Ic = hFE * Ib.
• Emitter: Acts as the exit for the controlled current.
Modes of Operation:
• Cut-off Region: Base-emitter junction is not forward biased. No conduction.
• Active Region: Base-emitter junction is forward biased; collector-emitter junction reverse biased. Perfect for amplification.
• Saturation Region: Both junctions forward biased; transistor acts as a closed switch.
In switching applications, designers often intentionally "overdrive" the base current to ensure that the D882 enters saturation completely, minimizing collector-emitter voltage (Vce(sat)) and improving switching efficiency.
D882 Power Ratings
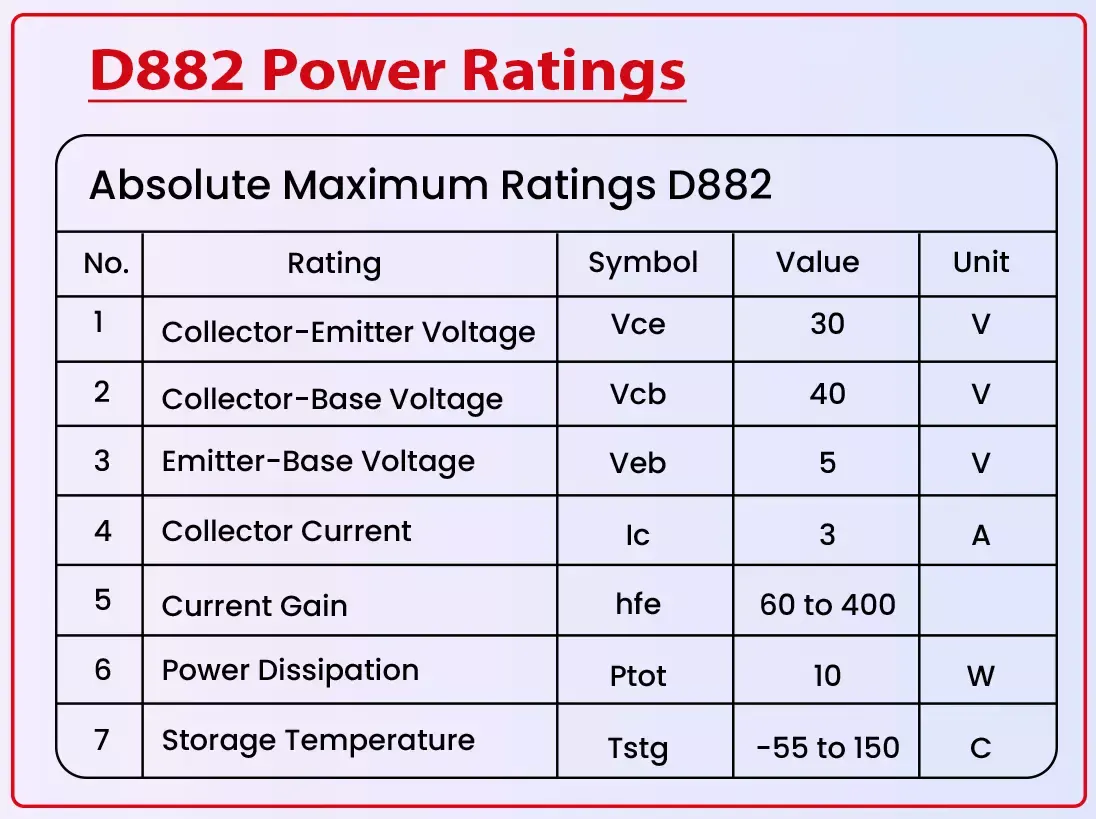
The D882 transistor is designed to handle moderate power levels, making it ideal for low to medium-power amplification and switching applications. Understanding the power ratings of the D882 is crucial for ensuring that it operates within its safe limits and doesn't experience overheating or failure. Below are the key power ratings and considerations for the D882:
| Parameter | Condition | Typical Value |
| Maximum Collector Current | Continuous | 3A |
| Peak Collector Current | Pulse width ≤ 5ms | 5A |
| Maximum Power Dissipation | At Tc=25°C (case temperature) | 10W |
| Derating Above 25°C | - | 80mW/°C |
| Thermal Resistance (junction to case) | - | 2°C/W |
Even though the D882 can dissipate 10W when properly cooled, practical applications rarely push it above 2W-5W continuously without an external heatsink. Always design conservatively for better longevity.
D882 Transistor Applications (Uses)
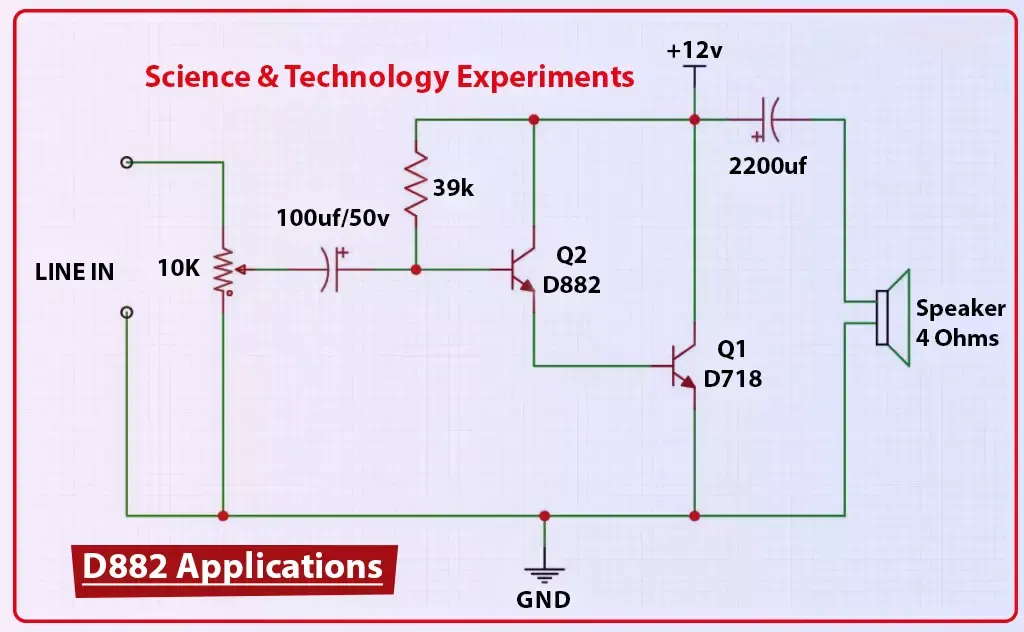
The D882 transistor is a versatile NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) that is widely used in various electronic applications. Its moderate power ratings, fast switching characteristics, and low cost make it an excellent choice for a range of circuits in both consumer and industrial electronics. Below, we’ll explore some of the most common and specialized uses of the D882 transistor.
The D882 finds uses across various fields. Here's a breakdown:
• Audio Amplifiers: Class AB output stages.
• Relay Drivers: Controlling high-current relays with microcontroller signals.
• DC Motor Drivers: Suitable for small motors in robotic and automation applications.
• Signal Amplification: Pre-amplifier stages in analog systems.
• Inverter Circuits: Key component in switching stages.
• Battery Chargers: Charge controllers for small to mid-sized batteries.
• Voltage Regulation: Linear regulators using D882 as pass elements.
• PWM Controllers: Pulse Width Modulated systems requiring fast switching.
Because of its frequency response and thermal resistance, the D882 is especially well-suited for audio amplifier circuits requiring tight thermal management and minimal distortion.
D882 Transistor Equivalent (Alternative) Parts
There are several transistors from different manufacturers that can serve as alternatives or equivalents to the D882, depending on the specific circuit requirements. Below is a list of equivalent transistors to the D882, categorized by similar specifications (such as current rating, voltage rating, and transistor type). Finding a good replacement is crucial when D882 is out of stock.
| Equivalent Transistor | Maximum Collector Current | Maximum Voltage | Gain Range (hFE) | Package |
| BD139 | 1.5A | 80V | 40-250 | TO-126 |
| 2N6488 | 4A | 60V | 40-160 | TO-220 |
| TIP31C | 3A | 100V | 10-50 | TO-220 |
| MJE3055T | 10A | 60V | 20-100 | TO-220 |
While BD139 and 2N6488 are popular alternatives, careful attention should be paid to gain and packaging. TO-220 versions offer better heat sinking but are bulkier than TO-126.
Where to Buy D882 Transistor
You can purchase the D882 transistor from a variety of online and physical electronic component distributors. Here are some popular platforms where you can find the D882 transistor. Finding authentic D882 units is important for critical applications:
• Official and Independent Distributors: Mouser, Digi-Key, RS Components and AIChipLink
• E-commerce Platforms: Amazon (beware of counterfeits), AliExpress (read reviews carefully)
• Local Electronics Stores: Good for urgent needs.
• Wholesale Markets: Shenzhen SEG Market, Huaqiangbei (for bulk purchases).
For important projects, always source from authorized distributors to ensure original parts. Clones might have lower current ratings than stated. Make sure to check the shipping fees and delivery times, especially if ordering from overseas. It's also important to verify that the D882 is the correct fit for your application by reviewing its datasheet and specifications.
Conclusion
The D882 transistor stands out as a reliable and affordable option for medium-power amplification and switching applications. With strong specifications, flexible application potential, and wide availability, it remains a go-to component for designers, engineers, and hobbyists alike. By understanding its datasheet parameters, proper handling of its thermal properties, and exploring equivalent options when needed, you can leverage the D882 to its fullest potential.
Its high frequency response, good current gain, and ease of use make it suitable for a variety of electronic projects, including amplification, switching, and low-power driving. However, it is best suited for applications where the power handling requirements are not too high, as it has limitations in current handling and saturation voltage. As electronics continue to evolve, the D882’s combination of performance and cost-efficiency ensures its place in modern designs.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
Q1: What type of transistor is D882?
• It is an NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) designed for medium-power applications.
Q2: How much current can the D882 handle?
• Up to 3A continuous, with a peak rating of 5A under short pulse conditions.
Q3: Can D882 be used in audio amplifiers?
• Absolutely. It is excellent for low to medium-power audio amplification.
Q4: What happens if the D882 is overheated?
• Performance degrades significantly, and in extreme cases, it can lead to thermal runaway and eventual failure.
Q5: Can I directly replace D882 with TIP31C?
• Sometimes, but TIP31C has a different package (TO-220) and lower gain, so adjustments may be necessary.
Q6: How to ensure D882 works efficiently in switching?
• Overdrive the base current slightly to ensure full saturation during ON states.
Q7: Is D882 suitable for battery-powered circuits?
• Yes, but ensure low standby leakage current requirements are satisfied.
Q8: What is the main advantage of TO-126 packaging?
• It provides good heat dissipation without the bulk of TO-220, perfect for space-constrained designs.
Q9: What voltage ratings are important when choosing a substitute?
• Always match or exceed the collector-emitter voltage (Vce) and collector current (Ic) ratings.
Q10: How to tell if a D882 is counterfeit?
• Poor labeling, unusual package color, and suspiciously low prices are red flags. Measure hFE to verify.
Written by Jack Zhang from AIChipLink.
AIChipLink, one of the fastest-growing global independent electronic component distributors in the world, offers millions of products from thousands of manufacturers, and many of our in-stock parts is available to ship same day.
We mainly source and distribute integrated circuit (IC) products of brands such as Broadcom, Microchip, Texas Instruments, Infineon, NXP, Analog Devices, Qualcomm, Intel, etc., which are widely used in communication & network, telecom, industrial control, new energy and automotive electronics.
Empowered by AI, Linked to the Future. Get started on AIChipLink.com and submit your RFQ online today!




